Officials from East Carolina University and University Health Systems of Eastern Carolina dedicated the East Carolina Heart Institute today. Several hundred invited guests joined leaders from the two organizations to celebrate the facility. The Heart Institute puts ECU and Pitt County Memorial Hospital “at the forefront of progress and the cutting edge of the future,â€Â said Dr. W. Randolph Chitwood, director of the East Carolina Heart Institute.
 “What we dedicate today is a concept called the East Carolina Heart Institute that encompasses these new facilities, dedicated to the people of this region, and to the physicians, researchers, educators and staff devoted to their care,â€Â said Chitwood, who is cardiothoracic surgery and vascular surgery at the Brody School of Medicine at ECU. He is also senior associate vice chancellor for health sciences at ECU.
“What we dedicate today is a concept called the East Carolina Heart Institute that encompasses these new facilities, dedicated to the people of this region, and to the physicians, researchers, educators and staff devoted to their care,â€Â said Chitwood, who is cardiothoracic surgery and vascular surgery at the Brody School of Medicine at ECU. He is also senior associate vice chancellor for health sciences at ECU.
The dedication ceremony, held at the East Carolina Heart Institute at ECU, capped more than four years of work to bring a world-class cardiovascular disease institute to eastern North Carolina. In 2004, the General Assembly approved $60 million for a research, education and outpatient care facility at ECU. Pitt County Memorial Hospital secured private funding for a $160 million bed tower. Today, leaders from the two organizations celebrated the end of construction on both facilities.

Many who attended the ceremony also toured the two facilities after the event ended. The crowd included local and state officials, donors and other friends of each organization.
The celebration marked “the most significant collaboration University Health Systems and East Carolina University have ever undertaken,â€Â said UHS CEO Dave McRae. “It’s the biggest step of a journey we started more than 30 years ago, when a small county hospital and a fledgling medical school committed to forming the world-class academic medical center we’re part of today,â€Â McRae said.
ECU and PCMH have been “joined at the hip†for decades, ECU Chancellor Steve Ballard said. “The East Carolina Heart Institute is the latest partnership between us, and it will make a major and lasting impact in eastern North Carolina, the entire state and beyond,â€Â Ballard said.
The new buildings aren’t the only sign of a new approach to heart disease for ECU and PCMH. The two organizations have also redefined their model for treating cardiovascular illnesses. Both have organized their clinical staffs around illnesses and disease processes, rather than following a traditional model based on academic specialties. That new model encourages more information-sharing among doctors and puts new emphasis on patients’ best interests, Chitwood said. “This new model of care delivery is an innovative way to blend the science and art of medicine so that we add value to the patient,â€Â Chitwood said.
The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in North Carolina justifies the massive investment in treating and researching heart and vascular illnesses. Cardiovascular disease is the second-leading cause of death in the state, and nearly a quarter of N.C. residents suffer from cardiovascular ailments.
Planning for the East Carolina Heart Institute dates to early 2003. ECU and PCMH held a groundbreaking for the Heart Institute in March 2006. In addition to the six-story 375,000-square-foot bed tower, the Heart Institute at Pitt County Memorial Hospitalspawned a pair of companion projects: construction of a massive central utility plant to power the new building and the relocation of Moye Boulevard.
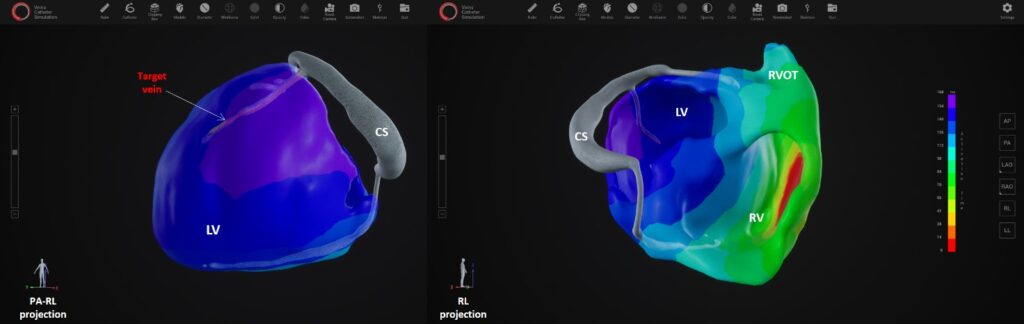
The Heart Institute at Pitt County Memorial Hospital has 120 cardiovascular beds, six operating rooms, seven interventional laboratories, three electrophysiology labs and a heart-healthy cafeteria, all designed to create the optimal patient care environment.
The four-story, 206,000-square-foot East Carolina Heart Institute at ECU houses science and clinical research, robotic-surgery training, future space for simulation laboratories, a clinical outpatient facility for cardiovascular diseases, a database center, offices and an auditorium.
The Heart Institute at Pitt County Memorial Hospital will open Jan. 5. ECU physicians have been seeing patients at the East Carolina Heart Institute at ECU since September. For more information please visit www.eastcarolinaheartinstitute.com
Via EPR Network
More Healthcare press releases
Â
 ITALY, 15-Jul-2025 — /EuropaWire/ — An EU‑funded consortium of Italian and French partners has unveiled PANDORA, a pioneering in‑silico platform designed to transform aortic aneurysm surgery, according to a recent press release announcement made on EuropaWire. Developed by LivGemini, RBF Morph, INSA and Université de Rennes (UnivREN) in collaboration with Rennes University Hospital, PANDORA creates patient‑specific “digital twins” of the aorta by combining AI‑driven image analysis, mesh‑morphing algorithms and high‑performance simulations.
ITALY, 15-Jul-2025 — /EuropaWire/ — An EU‑funded consortium of Italian and French partners has unveiled PANDORA, a pioneering in‑silico platform designed to transform aortic aneurysm surgery, according to a recent press release announcement made on EuropaWire. Developed by LivGemini, RBF Morph, INSA and Université de Rennes (UnivREN) in collaboration with Rennes University Hospital, PANDORA creates patient‑specific “digital twins” of the aorta by combining AI‑driven image analysis, mesh‑morphing algorithms and high‑performance simulations.